In today’s digital landscape, optimizing search engine visibility is paramount for websites seeking to attract organic traffic. When managing website pages and optimizing search engine visibility, two standard terms often come up: nofollow and noindex. These attributes determine how search engines crawl and index web pages.
Let’s say you have a personal blog and don’t want search engines to show it to everyone. You can use the “noindex” code to tell search engines to keep your journal private, so it won’t appear when people search for it. It’s like having a secret hiding place for your journal; only you have the key!
Similarly, imagine you have a list of incredible websites you want to share with your friends, but you don’t want the search engines to think you endorse those websites. Using the “nofollow” code, you can tell the search engines not to pass on your website’s authority to those links. It’s like saying, “Hey, search engine, I’m just sharing these websites, but they don’t reflect my website’s importance or popularity.
In short, nofollow manages link authority, while noindex controls page visibility. To understand this deeper, we’ll delve into noindex nofollow meanings, how they appear in the source code of a web page, how they affect SEO and noindex vs. nofollow & what are their usage scenarios & more.
What Is Nofollow?
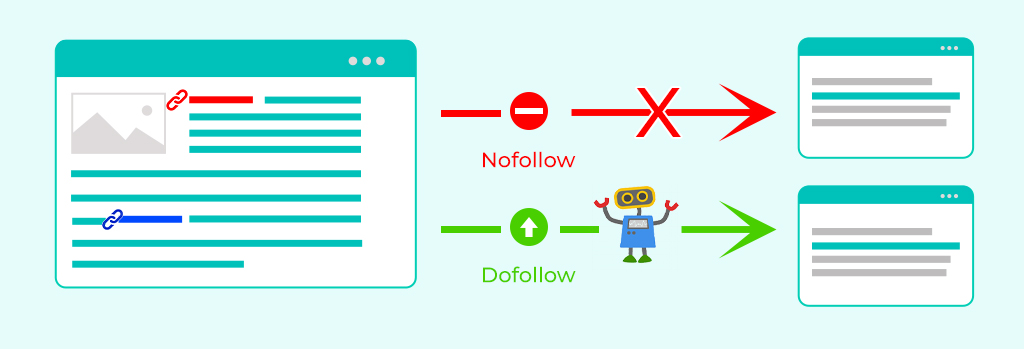
Nofollow is an HTML attribute (denoted by the “rel=nofollow” attribute in HTML) instructing search engine crawlers not to follow or pass any link equity from one web page to another. Search engines introduced it to com+bat spammy link-building practices and control link authority flow.
Nofollow is typically used on external links, user-generated content, or any link webmasters don’t want search engines to associate with their website’s authority. Its primary purpose is to combat spammy link-building practices and maintain control over a website’s link profile.
Nofollow Code Example:-
Example of how Nofollow appears in the source code of a web page:
<a href=”https://example.com” rel=”nofollow”>Click here</a>
What Is Noindex?
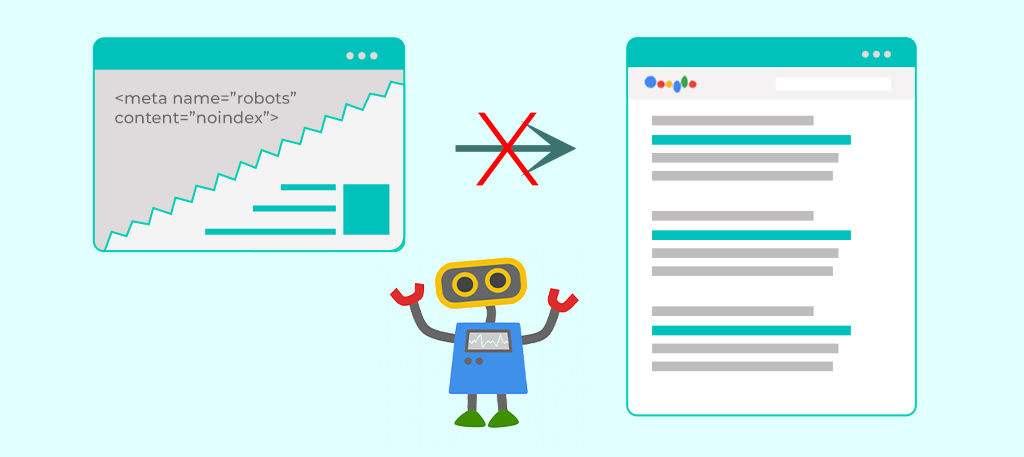
Noindex is a meta tag that instructs search engines not to index a particular web page. When a page is marked with noindex, it remains invisible in search engine result pages. This can be useful for pages that contain duplicate content, temporary pages, or private pages that are not intended to be visible in SERPs.
Noindex Code Example:-
Example of how Noindex appears in the source code of a web page:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Alternatively, the noindex directive can be implemented through a field in an HTTP response header. To do so, the following code must be added to the HTTP response header:
X-Robots-Tag: noindex
X-Robots-Tag: noindex Understand The Difference Between Nofollow and Noindex:
To understand the key differences between nofollow and noindex, let’s compare them in the following table:
| Nofollow | Noindex |
| This applies to individual links | This applies to entire web pages |
| Instructs search engines not to follow the linked page | Instructs search engines not to include the page in search results |
| Used to manage link authority and combat spam | Used to control page visibility and prevent indexing |
| Applied through the rel=”nofollow” attribute | Applied through the <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> meta tag |
| Typically used on external links or user-generated content | Used for pages with duplicate content, temporary pages, or private pages |
| Does not affect page indexing or visibility | Directly affects page indexing and visibility in search results |
Common Uses Of Noindex Pages & Nofollow:
A. Nofollow Usage Scenarios:
1. External links:
Nofollow is frequently used on external links, particularly when a website owner does not want to pass link authority to the linked page. Nofollow is often the case for sponsored or paid links, user-generated content, or links the website owner does not want to endorse.
2. User-generated content:
Websites that allow users to contribute & market content, such as comments, forum posts, or guest blog submissions, may apply the nofollow attribute to those user-generated links. Nofollow helps prevent spam and manipulative link-building practices while maintaining control over the website’s link profile.
3. Advertising and sponsored content:
Nofollow is commonly used on links within advertisements, sponsored posts, or affiliate marketing content. Nofollow ensures compliance with search engine guidelines and avoids penalties for manipulating search rankings through paid links.
4. Untrusted or unverified links:
If a website owner is unsure about the credibility or safety of a particular link, they may choose to apply the nofollow attribute as a precautionary measure. Nofollow helps protect their website from potentially harmful or spammy links.
It’s worth noting that while nofollow provides a hint to search engines not to follow a link, it does not guarantee that search engines will completely ignore the link. Search engines can choose to crawl and analyze the link, but they won’t pass any link authority or use it as a ranking factor.
B. Common Noindex Pages:
1. Duplicate content pages:
When a website has multiple pages with identical or similar content, it’s essential to prevent search engines from indexing all of them to avoid diluting the site’s search relevance. Canonical tags or the noindex tag can be used to designate the preferred version of the content and prevent the indexing of duplicate pages.
2. Private or login-required pages:
Pages that require user authentication or access credentials, such as member-only areas, private forums, or subscription-based content, are often marked with a noindex tag. Noindex tag ensures that these pages remain hidden from search engine results. Moreover, you must audit your website thoroughly to identify the other technical SEO tactics you can apply.
3. Staging or development pages:
Websites often have staging or development environments where new features or design changes are tested before being pushed to the live site. These pages are typically noindexed to prevent search engines from indexing incomplete or unfinished content.
4. Thin or low-quality content pages:
Pages with low-quality or thin content providing minimal value to users may be marked with a noindex tag to prevent them from appearing in search results. Noindex tags can include placeholder pages, low-quality landing pages, or pages with little relevant information.
Conclusion: Difference Between Nofollow And Noindex
It’s important to know the difference between a nofollow and a noindex when it comes to managing your website. Nofollow is when search engines don’t follow certain links, and noindex is when pages don’t appear in search results. Knowing the difference between the two is key to ensuring you’re doing everything you can to ensure your website is optimized for search engines.
Nofollow manages link authority, while noindex controls page visibility. SEO services can boost your website’s ranking and business growth through comprehensive analysis, targeted keyword research, optimization, content creation, and performance monitoring. Their expertise ensures increased visibility, higher rankings, and organic traffic.
Partnering with GoFirstPage maximizes your website’s potential, helping you stay ahead of the competition, attract more customers, and achieve long-term success. Take advantage of the opportunity to optimize your website and drive sustainable growth. Contact GoFirstPage today for tailored SEO strategies.
Answers To Common Questions: Quick Overview
Why should I use the nofollow attribute on external links?
The nofollow attribute is essential for maintaining control over your business website’s link profile and preventing the transfer of link authority to external pages. When you use nofollow on external links, search engines understand that you don’t want to associate your website’s authority with the linked page. This attribute benefits sponsored or paid links, user-generated content, or any links you want to be cautious about.
Can I use the noindex attribute to hide certain pages from search engines without affecting the rest of my website?
Absolutely yes! The noindex attribute allows you to selectively hide specific pages from SERPs without impacting the indexing or visibility of the rest of your website. By applying the noindex meta tag to individual pages, such as duplicate content pages or private login-required pages, you can effectively prevent those pages from appearing in search results.
What happens if I accidentally apply nofollow and noindex to a web page?
If the nofollow and noindex attributes are mistakenly applied to a web page, it can have unintended consequences. Meanwhile, the noindex attribute explicitly instructs search engines not to index the page. As a result, the affected web page may not receive proper visibility in search results, and any outbound links on that page may not be crawled or indexed. Reviewing and correctly implementing these attributes carefully is crucial to avoid such issues. Need help with a proper website audit? Call us now @ +1 (917) 277-7780
Are there any negative effects of using the nofollow attribute excessively?
Applying nofollow to too many external links across your website might raise suspicions and affect the natural flow of link authority. Search engines might interpret an excessive use of nofollow as an attempt to manipulate search rankings or hide paid links. It’s essential to strike a balance and use nofollow where it serves a purpose, such as on sponsored or user-generated content, while allowing natural link authority flow for other relevant and trusted external links.
Can I selectively use the noindex attribute for specific sections or elements within a web page?
The noindex attribute is typically applied at the page level rather than on specific sections or elements. Its purpose is to control the indexing and visibility of the entire page. However, you can achieve similar results by using JavaScript techniques to dynamically load or remove content from a page based on user interaction. Whatever approach you apply, ensure proper functionality and compliance with search engine guidelines.
How long do search engines recognize the nofollow or noindex attributes?
The time search engines take to recognize and respect the nofollow or noindex attributes can vary. Once a search engine crawls a page and detects the presence of the nofollow or noindex attribute, it will process that information and adjust its behavior accordingly. However, the exact timing of these updates can depend on various factors, including the crawl frequency of the search engine, the popularity of the website, and the rate of changes on the page.
Does using the noindex attribute affect the internal links within a web page?
No, using the noindex attribute on a web page does not directly affect the internal links within that page. The noindex attribute explicitly instructs search engines not to index the page, meaning it will not appear in search results. However, internal links within the page will still be crawled and indexed unless marked with the nofollow attribute. The noindex attribute affects the page’s indexing, not altering the internal link structure or impacting search engine crawling and indexing.
Are there any SEO best practices when deciding between nofollow and noindex for specific situations?
When deciding between nofollow and noindex, it’s crucial to consider your specific goals and requirements. Here are some SEO best practices to guide your decision-making:
– Use nofollow for external links you don’t want to associate with your website’s authority, such as sponsored or paid links.
– Use noindex tag for pages with duplicate content, temporary or private pages that should not appear in SERPs. – Be selective in applying nofollow to user-generated content to prevent spam and maintain a reputable link profile.
– Avoid using nofollow excessively, as it can potentially impact natural link authority flow.
– Regularly review and update your nofollow & noindex directives based on changes to your website’s content and requirements.
Can search engines still discover and crawl a page marked with the noindex attribute if it is linked to other indexed pages?
Yes, search engines can still discover and crawl a page marked with the noindex attribute if linked to other indexed pages. Search engines may follow those links and access the page. However, they will respect the noindex directive and refrain from including the page in their search results. Need help with a thorough website audit & SEO audit? Contact us now @ +1 (917) 277-7780 or email us at info@gofirstpage.com to achieve higher rankings on SERPs.